Windows 11’s hibernation feature saves your current work state and lets you resume anytime you want without keeping your machine turned on. I’ll explain how this feature works, when you should use it, and how to enable it on your computer.
What Is Hibernation?
Hibernation is a Windows feature that offloads all the data in the RAM and stores that data in a local file on your hard drive or SSD. This saves your PC’s current state, like any open files, running apps, open windows, and so on. The file that this data gets saved in is named hiberfil.sys.
The next time you turn on your computer (come out of hibernation), you can quickly resume your work, as your PC automatically opens all the apps, files, and windows that were open before you entered hibernation.
When to Use Hibernation
Hibernation is useful in many scenarios. If you’re taking a long break from your PC but don’t want to re-open all your apps the next time, simply put your PC in hibernation mode. It’ll let you resume your work without much effort.
Note that hibernation works differently from Windows’ Sleep mode. In Sleep mode, your PC is still turned on, but in hibernation, your machine shuts down completely. This allows you to save battery on your laptop, as your laptop doesn’t use any battery when it’s in hibernation.
Sleep mode is useful when you’re taking a really short break from your PC, and hibernation is useful when you’re going to be away from your PC for several hours or longer.
Enable Hibernation on Windows 11
Turning on hibernation on Windows 11 is as easy as using one of the three methods listed below. You can use Command Prompt, PowerShell, or Registry Editor to turn on and off the mode. Here are all those methods.
Method 1: Using Command Prompt
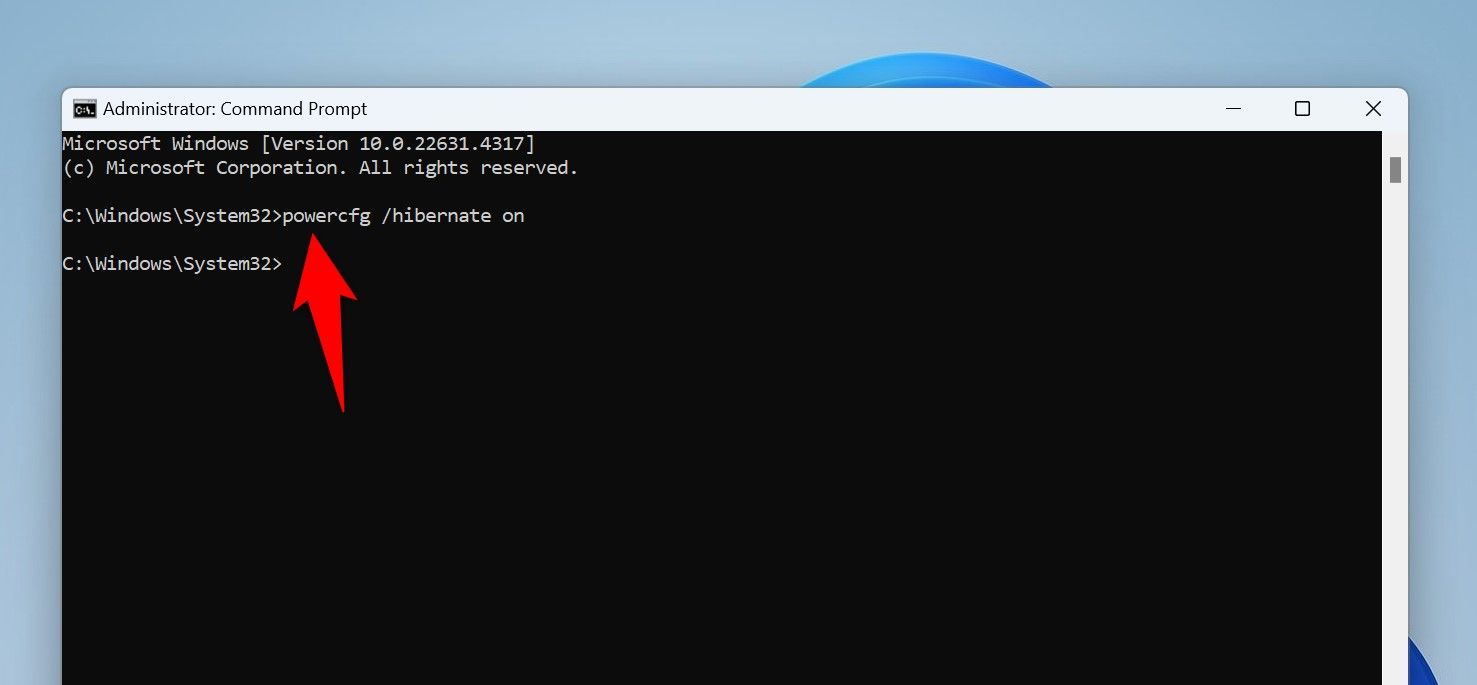
The easiest way to enable hibernation is by executing a command in Command Prompt. To do that, open Windows Search, type Command Prompt, and select “Run as Administrator.” In the User Account Control prompt, choose “Yes.”
On the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /hibernate on
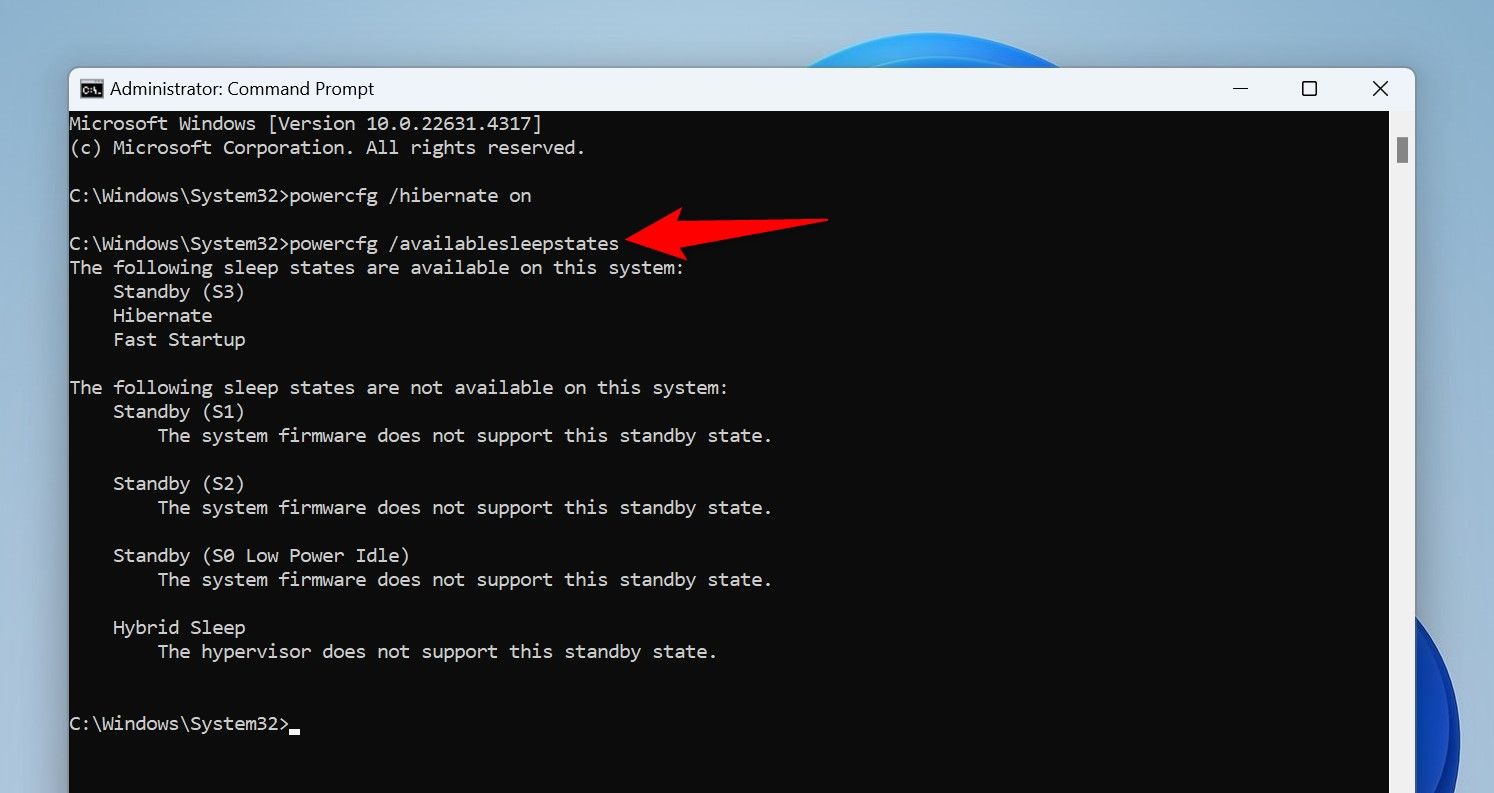
Hibernation is now enabled. To check the feature’s current state, run the following command:
powercfg /availablesleepstates
Hibernate will be one of the available sleep states.
Method 2: With PowerShell
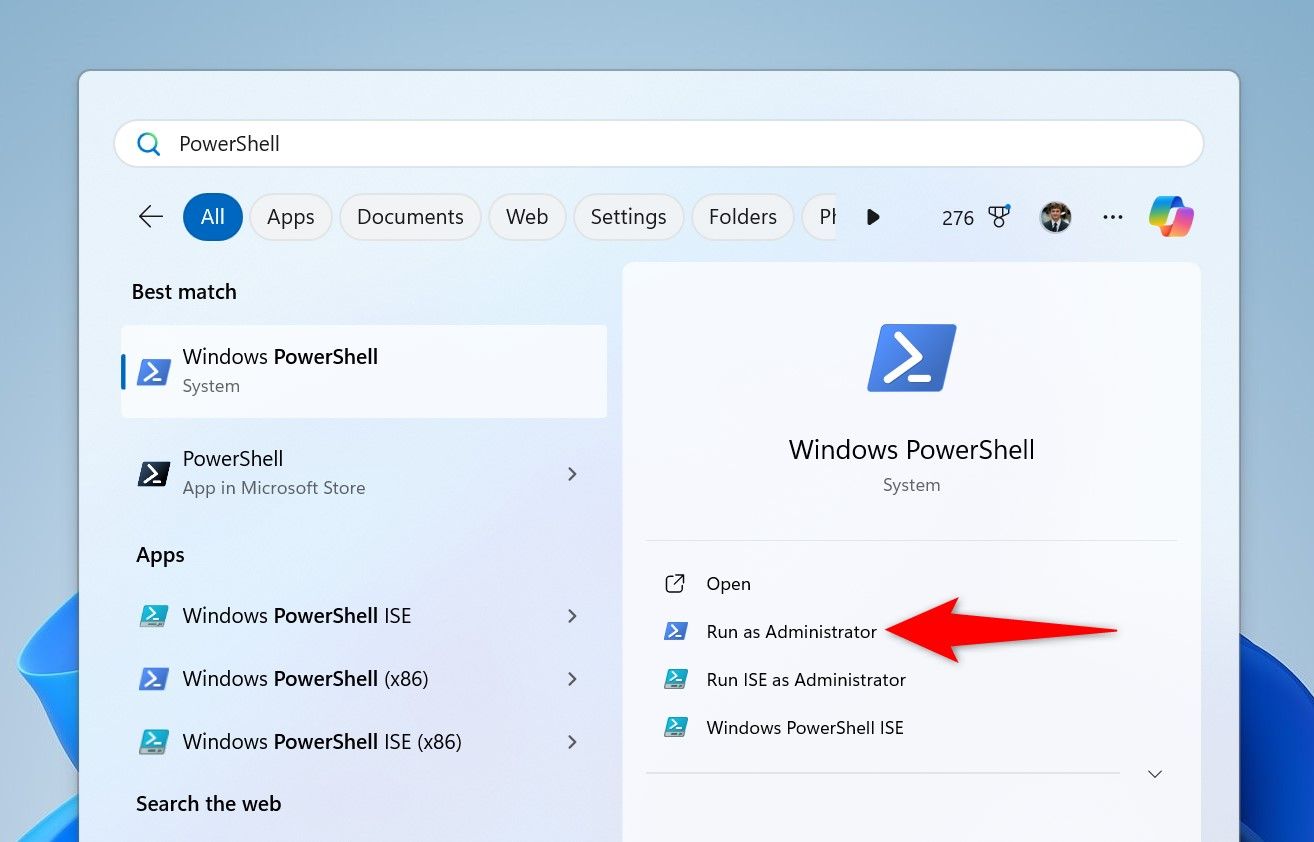
PowerShell is another way to turn on hibernation on Windows 11. Start by opening Windows Search, typing PowerShell, and choosing “Run as Administrator.” Select “Yes” in the User Account Control prompt.
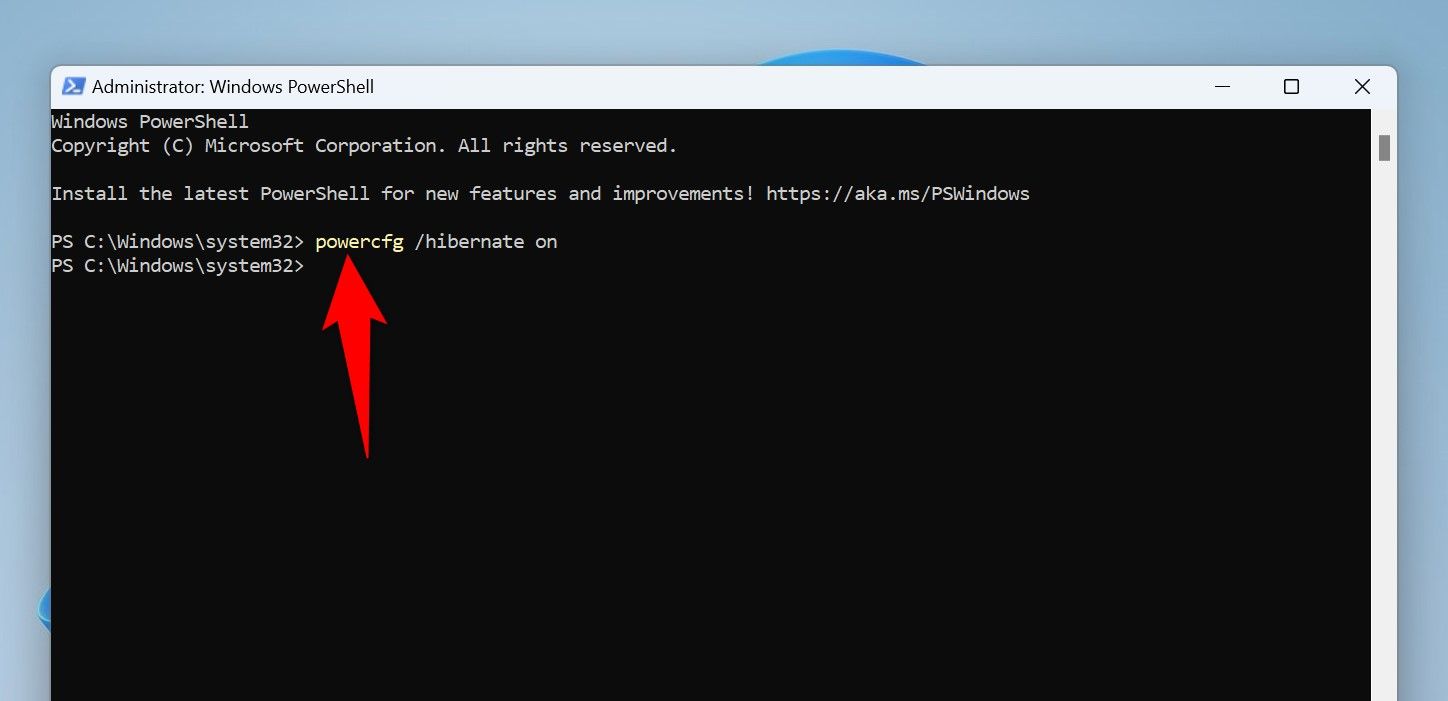
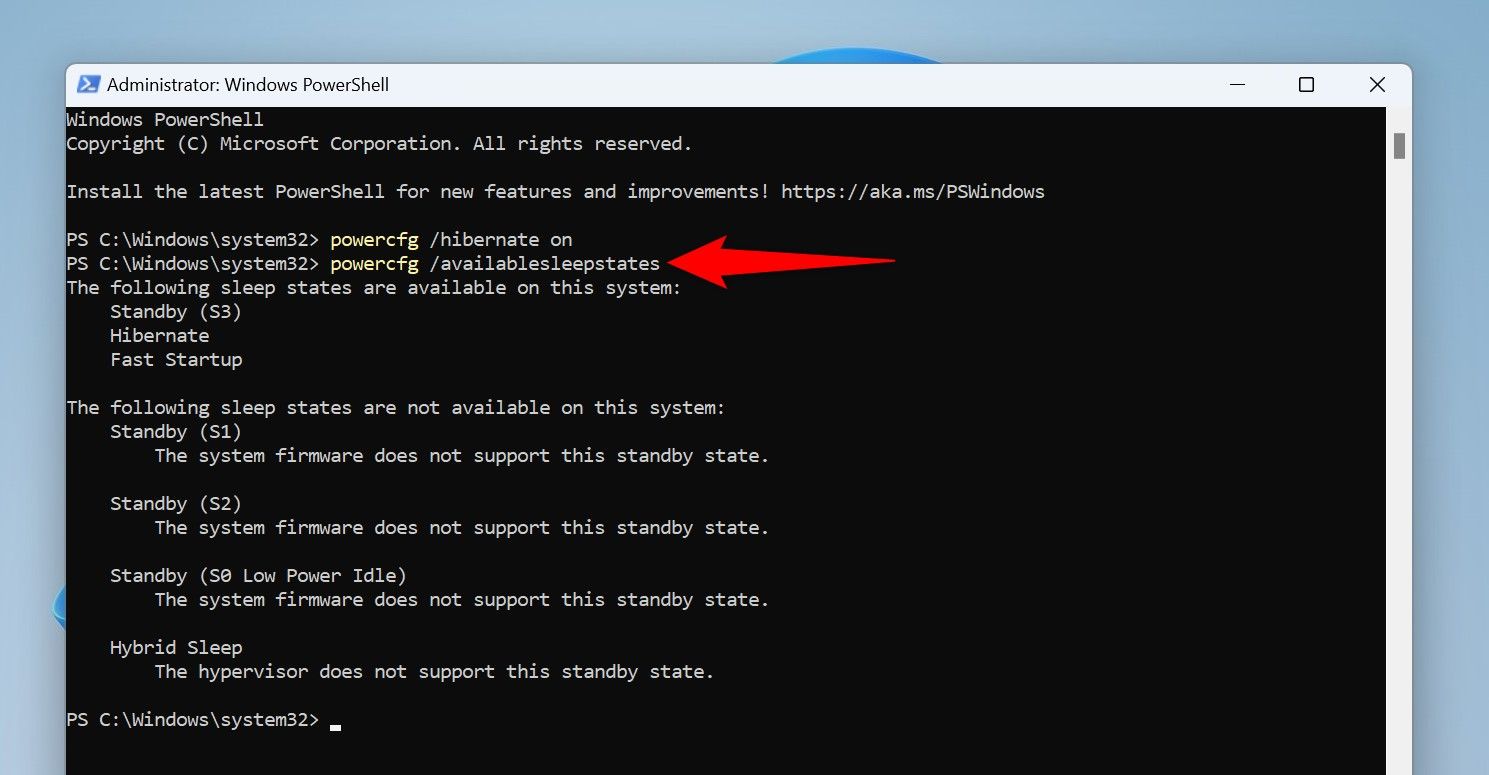
On the PowerShell window, type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /hibernate on
Hibernation is now activated. Verify the feature’s status by running the following command:
powercfg /availablesleepstates
The first section will tell you hibernation’s current status.
Method 3: Using Registry Editor
If you prefer graphical methods, use Registry Editor to change a registry item’s value that enables hibernation.
Only use this method if the above two methods don’t work for you. Making accidental changes in Windows registry can cause your system to be unstable.
Start by launching the Run dialog box using Windows+R. Type the following in the box and select “OK” or press Enter:
regedit
In the User Account Control prompt, select “Yes.” In Registry Editor, navigate to the following path.
To quickly get there, copy the path below, paste it in the Registry Editor’s path box, and press Enter.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power
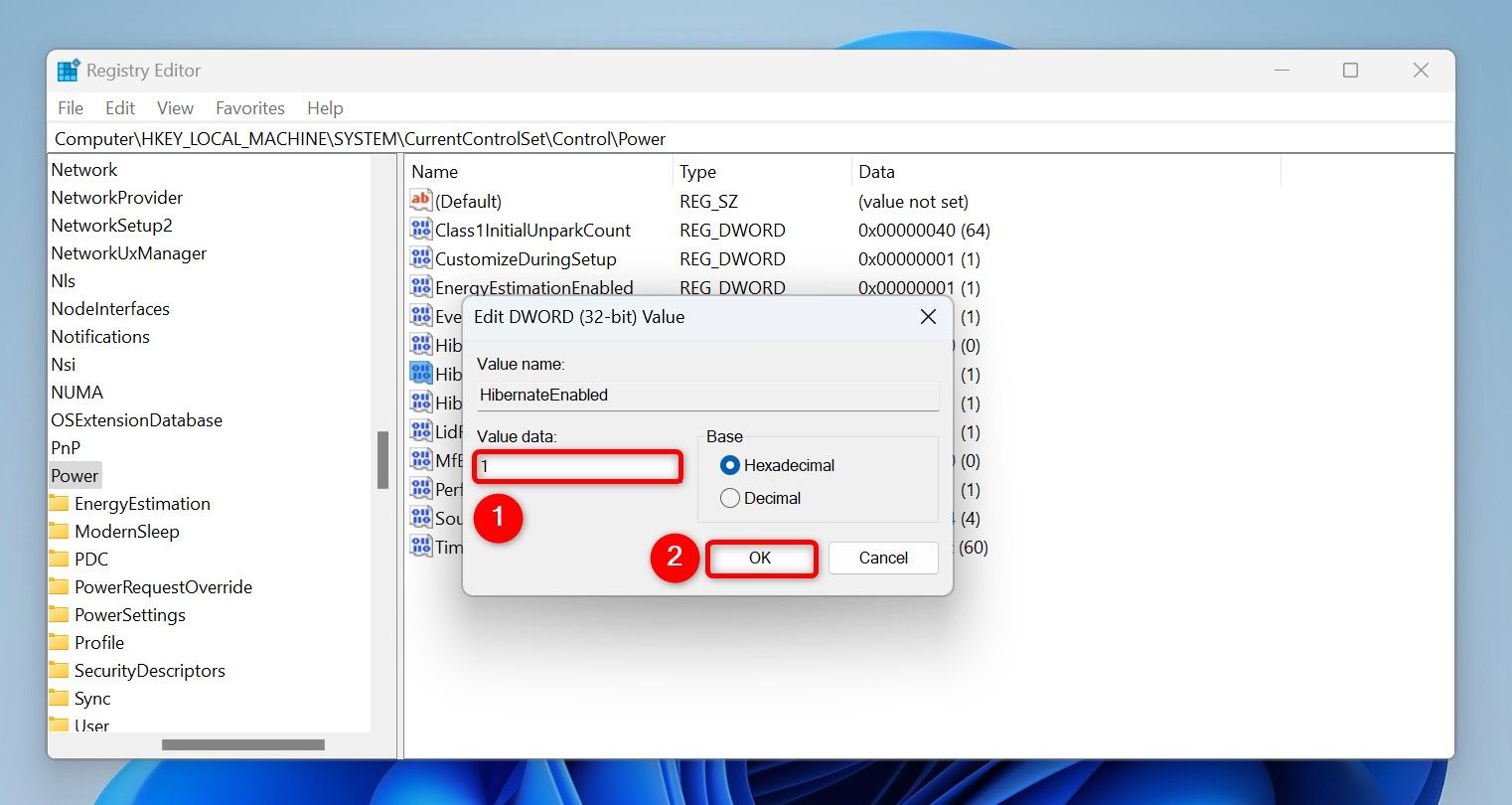
On the right pane, double-click the item that says “HibernateEnabled.” If you don’t find this item, create it by right-clicking, choosing New > DWORD (32-bit) Value, typing HibernateEnabled, and pressing Enter.
Type 1 in the “Value Data” field and select “OK.” Close Registry Editor and restart your Windows 11 PC.
Hibernation is now enabled.
Change a Hibernation Option in Control Panel
To enable the option to put your PC in hibernation mode, make a change in Control Panel as follows.
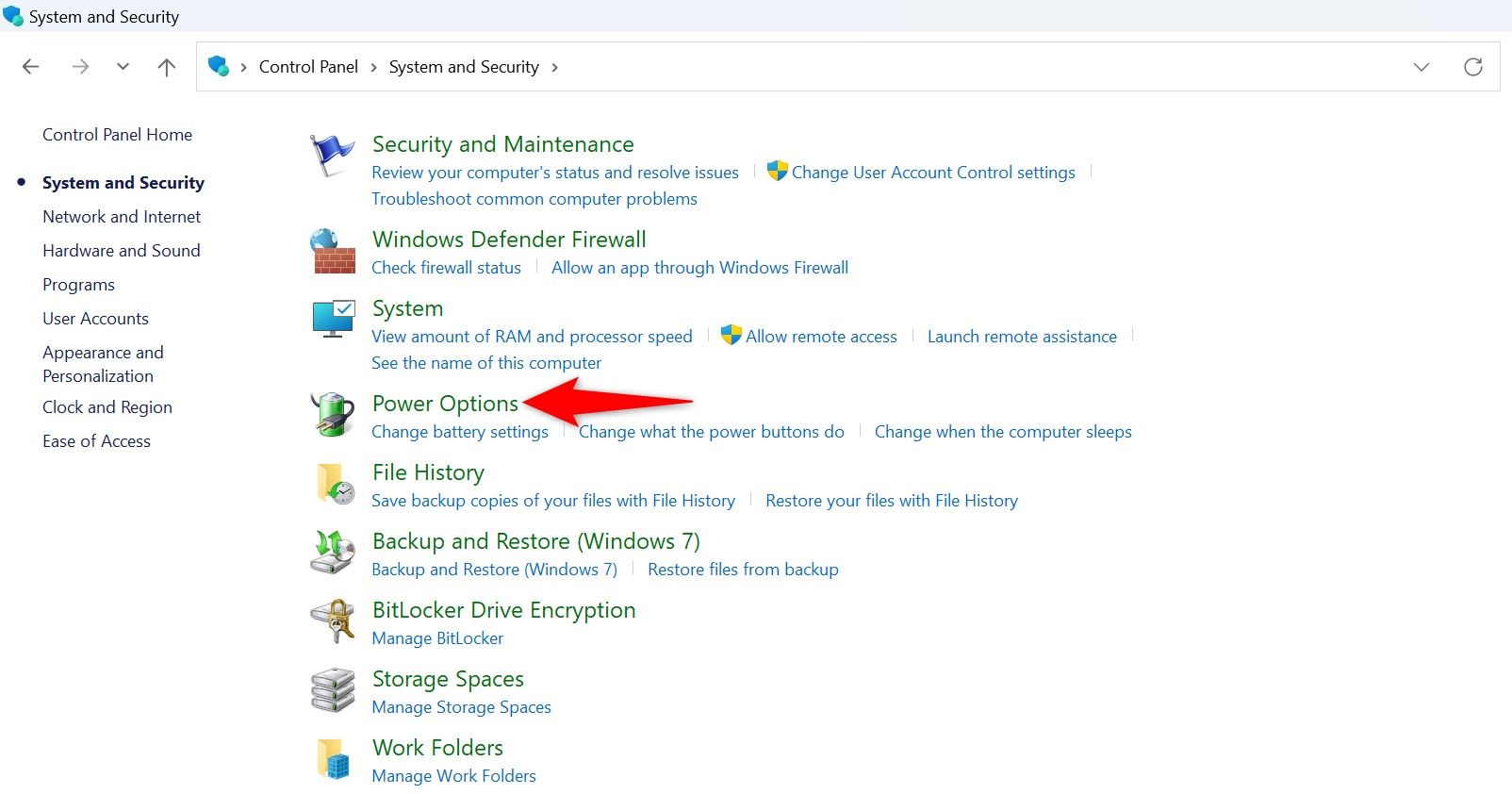
Launch Windows Search, type Control Panel, and select the utility. Choose System and Security > Power Options in Control Panel.
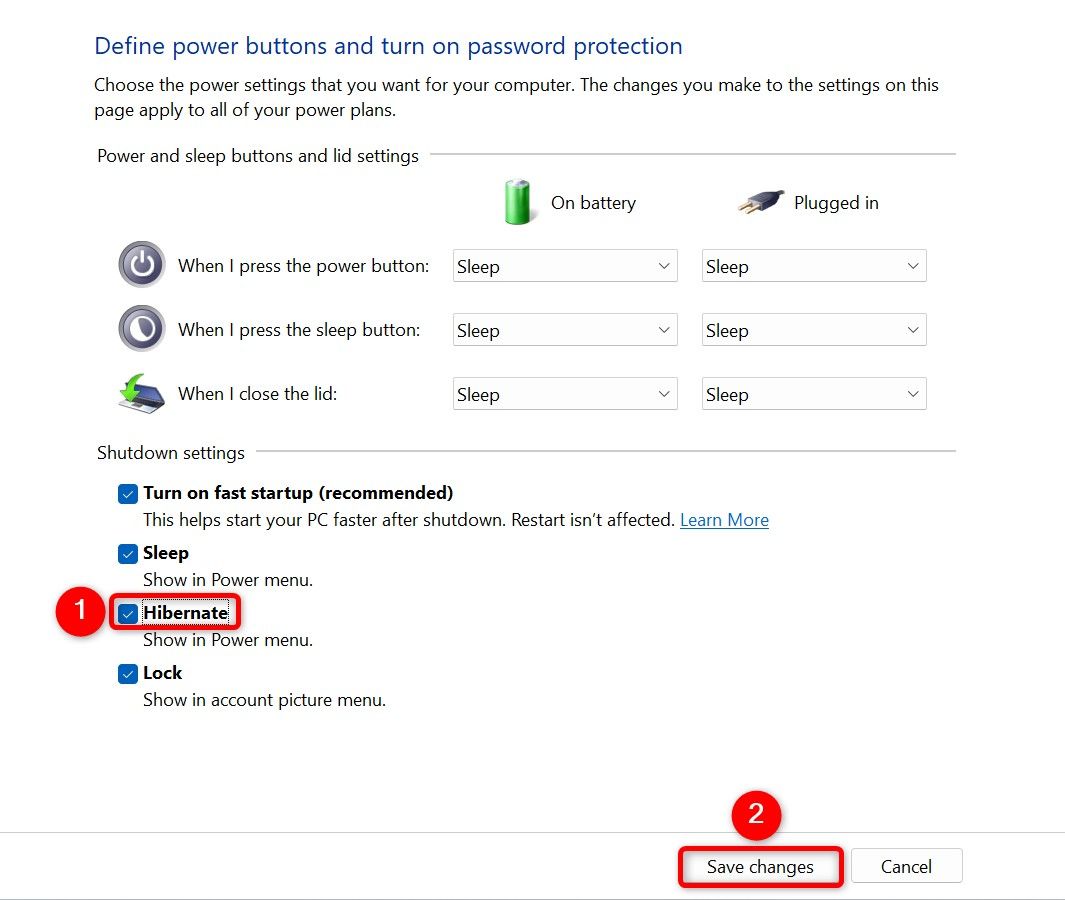
From the left sidebar, select “Choose What the Power Buttons Do.” Select “Change Settings That Are Currently Unavailable” at the top. In the Shutdown Settings section, enable the “Hibernate” option. Then, select “Save Changes.”
If you want your machine to enter hibernation mode when you press the Power button or close your laptop’s lid, select the “Hibernate” option from the appropriate drop-down menu.
And that’s it.
What to Do if You Don’t See the Hibernation Option?
If you don’t see the option to put your PC in hibernation mode in the Power menu, your current power settings might have an issue. In this case, reset the power plan settings as follows to fix the problem.
Open Windows Search, type Command Prompt, and select “Run as Administrator.” Choose “Yes” in the User Account Control prompt. Type the following command in CMD and press Enter:
powercfg /restoredefaultschemes
What to Do if the Hibernation File Uses Too Much Storage?
Since hibernation stores all the content from the RAM on a local file, the larger your RAM size, the larger the hibernation file will be. If you’re running out of space on your PC, luckily, you can shrink the hibernation file. Windows allows you to make the hibernation file use less space by removing additional hibernation features like hybrid sleep.
To do that, open Windows Search, type Command Prompt, and select “Run as Administrator.” Choose “Yes” in the User Account Control prompt.
On the CMD window, type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /h /type reduced
After executing the command, close the Command Prompt window.
And that’s how you use a built-in Windows 11 feature to save your machine’s battery without having to start your work from scratch. Enjoy!
Source link