The End of Opioids? New Drug Could Change the Way We Treat Severe Pain
The discovery of a new painkiller offers relief with fewer side effects.
Morphine and other opioids are commonly used in medicine because of their strong ability to relieve pain. Yet, they also pose significant risks, including respiratory depression and drug dependence. To limit these dangers, Japan enforces strict rules that allow only specially authorized physicians to prescribe such medications.
In contrast, the United States saw widespread prescribing of the opioid OxyContin, which fueled a rise in the misuse of synthetic opioids like fentanyl. By 2023, deaths from opioid overdoses had exceeded 80,000, marking the escalation of a nationwide public health emergency now known as the “opioid crisis.”
A new analgesic approach
Opioids may soon face competition. Researchers at Kyoto University have identified a new analgesic, named ADRIANA, that provides pain relief through a completely different biological pathway. The drug is now moving through clinical development as part of an international research collaboration.
“If successfully commercialized, ADRIANA would offer a new pain management option that does not rely on opioids, contributing significantly to the reduction of opioid use in clinical settings,” says corresponding author Masatoshi Hagiwara, a specially-appointed professor at Kyoto University.
Targeting adrenoceptors for safer pain relief
The researchers drew their initial inspiration from compounds that imitate noradrenaline, a chemical released during life-threatening situations that activates α2A-adrenoceptors to reduce pain. While effective, these compounds carry a high risk of destabilizing cardiovascular function. By examining the relationship between noradrenaline levels and α2B-adrenoceptors, the team proposed that selectively blocking α2B-adrenoceptors could increase noradrenaline activity, stimulate α2A-adrenoceptors, and provide pain relief without triggering cardiovascular instability.
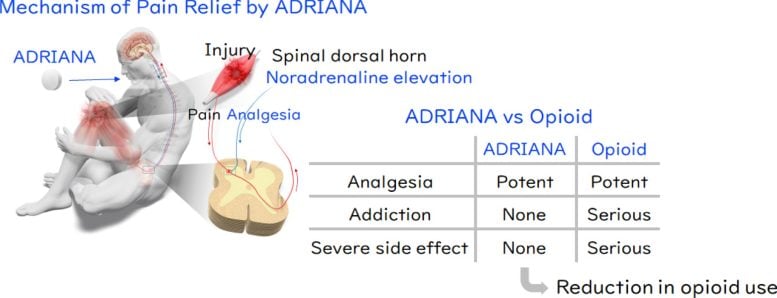
To test this idea, the scientists used a specialized method called the TGFα shedding assay, which allowed them to measure the function of different α2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Through compound screening, they succeeded in identifying the world’s first selective α2B-adrenoceptor antagonist.
Promising clinical results and future trials
After success in administering the compound to mice and conducting non-clinical studies to assess its safety, physician-led clinical trials were conducted at Kyoto University Hospital. Both the Phase I trial in healthy volunteers and the Phase II trial in patients with postoperative pain following lung cancer surgery yielded highly promising results.
Building on these outcomes, preparations are now underway for a large-scale Phase II clinical trial in the United States, in collaboration with BTB Therapeutics, Inc, a Kyoto University-originated venture company.
As Japan’s first non-opioid analgesic, ADRIANA has the potential not only to relieve severe pain for patients worldwide but could also play a meaningful role in addressing the opioid crisis — a pressing social issue in the United States — and thus contribute to international public health efforts.
“We aim to evaluate the analgesic effects of ADRIANA across various types of pain and ultimately make this treatment accessible to a broader population of patients suffering from chronic pain,” says Hagiwara.
Reference: “Discovery and development of an oral analgesic targeting the α2B adrenoceptor” by Masayasu Toyomoto, Takashi Kurihara, Takayuki Nakagawa, Asuka Inoue, Ryo Kimura, Isao Kii, Teruo Sawada, Takashi Ogihara, Kazuki Nagayasu, Takayuki Kishi, Hiroshi Onogi, Dohyun Im, Hidetsugu Asada, So Iwata, Jumpei Taguchi, Yuto Sumida, Suguru Yoshida, Junken Aoki, Takamitsu Hosoya and Masatoshi Hagiwara, 7 August 2025, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2500006122
Funding: Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Japan Science and Technology Agency, Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
Source link

